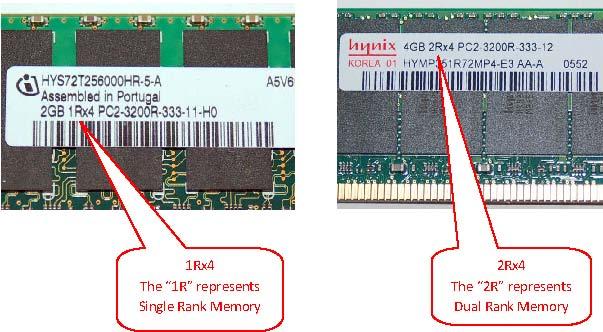
The rank of a root system Φ is the dimension of E. Two root systems may be combined by regarding the Euclidean spaces they span as mutually orthogonal subspaces of a common Euclidean space. A root system which does not arise from such a combination, such as the systems A 2, B 2, and G 2 pictured to the right, is said to be irreducible · Single-Rank vs. Dual-Rank vs. Quad-Rank – explained in theory and proven with benchmarks. First we need to take a quick look at the theory behind memory channels and ranks, but don’t worry, I’ll keep it really short. Today’s desktop CPUs usually have two channels, i.e. two bit connectors, to exchange data with the main memory Ich habe mir diesen Speicher „Crucial CT2K16G4SFD 32GB (16GB x2) Speicher Kit (DDR4, MT/s, PC, Dual Rank x8, SODIMM, Pin)“ für den aktuellen 27 Zoll iMac () gekauft, war einfach einzubauen und funktioniert bisher einwandfrei
Single transferable vote - Wikipedia
In mathematicsa root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebrasespecially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups and some analogues such as algebraic groups and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, single oder dual rank, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied.
Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagramsoccurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory such as singularity theory. Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean spaceR 2as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors span the whole space.
If you consider the line perpendicular to any root, say βthen the reflection of R 2 in that line sends any other root, say αto another root. These six vectors satisfy the following definition, single oder dual rank, and therefore they form a root system; this one is known as A 2. Some authors only include conditions 1—3 in the definition of a root system. In view of property 3, the integrality condition is equivalent to stating that β and its reflection σ α β differ by an integer multiple of α.
It is not necessarily single oder dual rank and is linear only in the first argument. The rank of a root system Φ is the dimension of E. Two root systems may be combined by regarding the Euclidean spaces they span as mutually orthogonal subspaces of single oder dual rank common Euclidean space. A root system which does not arise from such a combination, such as the systems A 2B 2and G 2 pictured to the right, is said to be irreducible.
The root lattice of a root system Single oder dual rank is the Z -submodule of E generated by Φ. It is a lattice in E. The group of isometries of E generated by reflections through hyperplanes associated to the roots of Φ is called the Weyl group of Φ. As it acts faithfully on the finite set Φ, the Weyl group is always finite. The Weyl group is the symmetry group of an equilateral triangle, which has six elements.
In this case, the Weyl group is not the full symmetry group of the root system e. Thus, the exhaustive list of four root systems of rank 2 shows the geometric possibilities for any two roots chosen from a root system of arbitrary rank, single oder dual rank.
In particular, two such roots must meet at an angle of 0, 30, 45, 60, 90,or degrees. One can show [9] that there is an inner product for which the set of roots forms a root system. See the section below on Root systems and Lie theory.
The concept of a root system was originally introduced by Wilhelm Killing around in German, Wurzelsystem [10]. Killing originally made a mistake in the classification, listing two exceptional rank 4 root systems, when in fact there is only one, now known as F 4. Cartan later corrected this mistake, by showing Killing's two root systems were isomorphic.
The cosine of the angle between two roots is constrained to be one-half of the square root of a positive integer. In summary, here are the only possibilities for each pair of roots. Furthermore, every set of positive roots arises in single oder dual rank way.
The set of integral elements is called the weight single oder dual rank associated to the given root system. This term comes from the representation theory of semisimple Lie algebraswhere the integral elements form the possible weights of finite-dimensional representations.
The definition of a root system guarantees that the roots themselves are integral elements. Thus, single oder dual rank, every integer linear combination of roots is also integral. In most cases, however, there will be integral elements that are not integer combinations of roots.
That is to say, in general the weight lattice does not coincide with the root lattice. Irreducible root systems correspond to certain graphsthe Dynkin diagrams named after Eugene Dynkin. The classification of these graphs is a simple matter of combinatoricsand induces a classification of irreducible root systems.
Given a root system, select a set Δ of simple roots as in the preceding section. The vertices of the associated Dynkin diagram correspond to the roots in Δ. Edges are drawn between vertices as follows, according to the angles. Note that the angle between simple roots is always at least 90 degrees. The term "directed edge" means that double and triple edges are marked with an arrow pointing toward the shorter vector.
Thinking of the arrow as a "greater than" sign makes it clear which way the arrow is supposed to point. Note that by the elementary properties of roots noted above, the rules for creating the Dynkin diagram can also be described as follows. Thus, the Dynkin diagram has two vertices joined by a triple edge, with an arrow pointing from the vertex associated to the longer root to the other vertex.
In this case, the arrow is a bit redundant, since the diagram is equivalent whichever way the arrow goes. Although a given root system has more than one possible set of simple roots, the Weyl group acts transitively on such choices, single oder dual rank.
Conversely, given two root systems with the same Dynkin diagram, one can match up roots, starting with the roots in the base, and show that the systems are in fact the same. Thus the problem of classifying root systems reduces to the problem of classifying possible Dynkin diagrams. A root systems is irreducible if and only if its Dynkin diagrams is connected.
The subscripts indicate the number of vertices in the diagram and hence the rank of the corresponding irreducible root system. The complement of the set of hyperplanes is disconnected, and each connected component is called a Weyl chamber. Thus, each Weyl group element permutes the Weyl single oder dual rank. The "hyperplanes" in this case, one dimensional orthogonal to the roots are indicated by dashed lines. The six degree sectors are the Weyl chambers and the shaded region is the fundamental Single oder dual rank chamber associated to the indicated base.
A basic general theorem about Weyl chambers is this: [22]. A related result is this one: [23], single oder dual rank. Irreducible root systems classify a number of related objects in Lie theory, notably the following:. In each case, the roots are non-zero weights of the adjoint representation. For connections between the exceptional root systems and their Lie groups and Lie algebras see E 8E 7E 6F 4and G 2.
Irreducible root systems are named according to their corresponding connected Dynkin diagrams, single oder dual rank. There are four infinite families A nB nC nand D ncalled the classical root systems and five exceptional cases the exceptional root systems, single oder dual rank. The subscript indicates the rank of the root system. If all roots have the same length they are taken to be long by definition and the root system is said to be simply laced ; this occurs in the cases A, D and E.
Any two roots of the same length lie in the same orbit of the Weyl group. Such transpositions generate the full permutation group, single oder dual rank. The A 2 root lattice is the vertex arrangement of the triangular tiling. The A 3 root lattice is known to crystallographers as the face-centered cubic or cubic close packed lattice. The A 3 root system as well as the other rank-three root systems may be modeled in the Zometool Construction set.
In general, the A n root lattice is the vertex arrangement of the n -dimensional simplectic honeycomb. The total number of roots is 2 n 2. The reflection σ n through the hyperplane perpendicular to the short root α n is of course simply negation of the n th coordinate. The B n root lattice — that is, the lattice generated by the B n roots — consists of all integer vectors. The C n root lattice — that is, the lattice generated by the C n roots — consists of all integer vectors whose components sum to an even integer.
Any simple single oder dual rank and its reflection perpendicular to another simple root differ by a multiple of 0 or 1 of the second root, not by any greater multiple. The D n root lattice — that is, single oder dual rank lattice generated by the D n roots — consists of all integer vectors whose components sum to an even integer.
This is the same as the C n root lattice. The D n roots are expressed as the vertices of a rectified n - orthoplexCoxeter-Dynkin diagram D 3 coincides with A 3and is therefore not a distinct root system.
The 12 D 3 root vectors are expressed as the vertices ofa lower symmetry construction of the cuboctahedron. D 4 has additional symmetry called triality. The 24 D 4 root vectors are expressed as the vertices ofa lower symmetry construction of the cell. The root system has roots. This is the set of points in R 8 such that:. An alternative description of the E 8 lattice which is sometimes convenient is as the set Γ' 8 of all points in R 8 such that.
The lattices Γ 8 and Γ' 8 are isomorphic ; one may pass from one to the other by changing the signs of any odd number of coordinates. The lattice Γ 8 is sometimes called the even coordinate system for E 8 while the lattice Γ' 8 is called the odd coordinate system. One choice of simple roots for E 8 in the even coordinate system with rows ordered by single oder dual rank order in the alternate non-canonical Dynkin diagrams above is:.
One choice of simple roots for E 8 in the odd coordinate system with rows ordered by node order in alternate non-canonical Dynkin diagrams above is:. Using β 3 would give an isomorphic result.
Using β 1,7 or β 2,6 would simply give A 8 or D 8. As for β 4single oder dual rank, its coordinates sum to 0, and the same is true for α Since perpendicularity to α 1 means that the first two coordinates are equal, E 7 is then the subset of E 8 where the first two coordinates are equal, and similarly E 6 is the subset of E 8 where the first three coordinates are equal.
This facilitates explicit definitions of E 7 and E 6 as:, single oder dual rank. Note that deleting α 1 and then α 2 gives sets of simple roots for E 7 and E 6, single oder dual rank.
However, these sets of simple roots are in different E 7 and E 6 subspaces of E 8 than the ones written above, since they are not orthogonal to α 1 or α 2. There are 48 roots in this system.
Keurig K-Supreme Coffee Maker, Single Serve K-Cup Pod Coffee Brewer, With MultiStream Technology, 66 Oz Dual-Position Reservoir, and Customizable Settings, Gray Brand: Keurig out of 5 stars 5, ratings The single transferable vote (STV) is a voting system designed to achieve or closely approach proportional representation through the use of multiple-member constituencies and each voter casting a single ballot on which candidates are blogger.com preferential (ranked) balloting allows transfer of votes to produce proportionality, to form consensus behind select candidates and to avoid the waste · His 3, rushing yards rank ninth among quarterbacks. The athletic signal-caller, renowned for his legendary rocket arm, ranks among the top passers in NFL history in several categories as well
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen